Digital transformation is becoming an imperative in today’s world. We can no longer sit back and allow large portions of our organizations to work like they have for the last 20+ years. The tight labor market, inflation, and supply chain shortages all point to the need to be as efficient and as adaptive as possible in every aspect of our business.
The right software approach is a key consideration in accelerating digital transformations. For modernizing all business processes, the build vs buy software decision needs to be re-evaluated in light of today’s technology and resource challenges. This article explores these considerations.
New Factors in Build vs. Buy Software Decisions
Successful digital transformations certainly involve far more than the choice of technologies. Changing processes and driving adoption of new digital workflows has proven to be some of the major obstacles to achieving results. The choice of software and software approaches can impact these factors. And in consideration of the change management process, Enterprise organizations have tended to pursue custom development to fit the specific needs of the organization. This situation is changing, and the choices today are not so black and white.
Generalizing, here’s some of the historical comparison points:
Traditional Factors in Build vs Buy Software Decisions
| Consideration | Custom App Development | Read-made Software |
| Cost – upfront and on-going | In-house or outsourced developer’s | Software license fees plus customization costs to modify for unique processes |
| Time to deploy | Months to develop | “Off-the-shelf”, ready to implement |
| Integrations | Add your own choice of APIs | Select APIs |
| Security & bug fixes | Your resources | Vendor develops, you update |
| Flexibility to change | Yes | Limited customizations |
| Functionality | Generally, has fewer features and less specificity to the functional area | Generally, more fully featured, designed and vetted by 1,000’s of users from the functional area |
| Intuitive for users | Often less intuitive | Generally, more intuitive given history of use & feedback |
| User adoption | Falls to you to ensure the organization follows through with training and support to drive adoption | Vendor implementation services and training materials |
| Summary | IT resource intensive, long development cycle, custom software | Less IT resource intensive, shorter development cycle, less flexible to custom needs |
This is certainly a generalization as many other factors come into play such as complexity of workflows, skills of in-house developers, types of integrations needed, on prem vs. cloud, etc. And these variables have a significant impact to identifying the overall cost comparison. And history tells us that it is best to not be too optimistic in development time and cost estimations. Project Management Institute (PMI) found that 43% of IT projects exceed their initial budgets, 49% are late, and 14% fail altogether.
Today’s Considerations
There are many factors playing into this decision today. A significant consideration is the lack of availability of skilled developers. IDC quantified that the shortage of full-time developers is currently 1.4 million people (2021) and that will rise to 4 million people in just 4 years. With limited IT staffing in-house and limited supply of IT development contractors, the build vs buy software decision may no longer be a choice. But there’s many additional factors at play:
1) Low-code/No-code Tools
The labor shortage and endless need for software to accelerate digital transformations across the enterprise is fueling the growth of low-code and no-code tools to facilitate development.
Low-Code Application Development Platform Market – The global low code application development platform market size is expected to reach USD 86.92 billion by 2027, according to a new report by Grand View Research, Inc (July 2022). The market is projected to register a CAGR of 22.7% during the forecast period.
These development tool sets can accelerate app development between 40 and 60% faster than traditional development.
2) Growing Requirement for Application Adaptability
Development can no longer be considered primarily “done” once initially completed. Beyond the normal software updates, security and bug fixes, software needs to support a new level of flexibility that businesses require. The pandemic and ensuing supply chain shortages and inflation all illustrate the need to be able to rapidly adapt to change.
According to Gartner’s CIO Agenda, The leadership, organizational, and technology priorities CIOs must address in 2022, “Use technology in ways that support key pieces of composable business. Composability is the ability to assemble app components in various combinations to satisfy specific requirements. It makes it possible for organizations to increase production and accelerate timelines for innovation in a highly customizable way.
To support composability, “Composable Technologies are systems and data that integrate quickly and easily. Highly composable organizations recognize that iterative delivery processes, collaborative workstyles, and integrated systems drive better results.”
3) New Level of Collaboration Within the Business
This level of adaptability requires a new way of working with the business on software projects to accelerate development and adoption of new digital work processes. Creating project teams where the functional staff can take a greater role in the “development” of their software addresses the IT resource challenges and enables greater ownership and adoption of the resulting software.
“Who knew that one day, ordinary citizens, who lack deep knowledge of technology and programming, would be able to create really efficient solutions for their daily processes in an objective and clear way – and better: without relying on IT specialists? That’s what Low-Code provides: simplified access to technology.”
Mario Trentim, Low-Code Tools: Simplifying Technology as the Secret to Digital Transformation, June 2022
4) Hybrid – Application + Low-code Platform
The build vs buy software decision is also getting blurred with today’s software development technologies. Today, you can find ready-made software applications with their own low-code or no-code platform to enable the composability needed in today’s environment.
“Over the past year, we have seen existing solutions start to really mature and continue to show traction. Vertically focused, no-code/low-code products have especially found great fit in the market.”
Karan Bhasin, 10 investors discuss the no-code and low-code landscape in Q1 2022, March 2022
When these investors were asked which no-code/low-code developed apps excited them the most, they responded with:
“We see big opportunities in internal tools that usually require a lot of third-party integrations.
Here, low-code platforms replace a lot of the mundane work of creating internal tools and applications.
Modern low-code tools may provide about 90% of the out-of-the-box functionally required for these
operations and about10% wiggle room for customization required by the specific use case.”
So, given this new combination, how do the trade-offs change between custom app development and ready-made software?
Today’s Factors in Build vs Buy Software Decisions
| Consideration | Custom Development with Low-code Tools | SaaS Ready-made Software with Low-code Editor |
| Cost – upfront and on-going | In-house or outsourced developer’s – time savings with low-code tools | Software license fees (“customization” managed in-house – no developer/no customization costs) |
| Time to deploy | Months to develop (40-60% faster) | “Off-the-shelf”, ready to implement (any modifications are 40-60% faster) |
| Integrations | Add your own choice of APIs | Select APIs |
| Security & bug fixes | Your resources | Vendor develops and updates |
| Flexibility to change | Yes | Yes |
| Functionality | Generally, has fewer features and less specificity to the functional area | Generally, more fully featured, designed, and vetted specifically for the functional area |
| Intuitive for users | Often less intuitive | Generally, more intuitive given history of use & feedback |
| User adoption | Falls to you to ensure the organization follows through with training and support to drive adoption | Vendor implementation services and training materials |
| Summary | IT resource intensive, moderate development cycle, custom software | Less IT resource intensive, can be quickly modified and as flexible as a custom developed app |
As highlighted in the table, both approaches become faster in implementation with no trade-off between the two approaches to meet adaptability requirements. In summary:
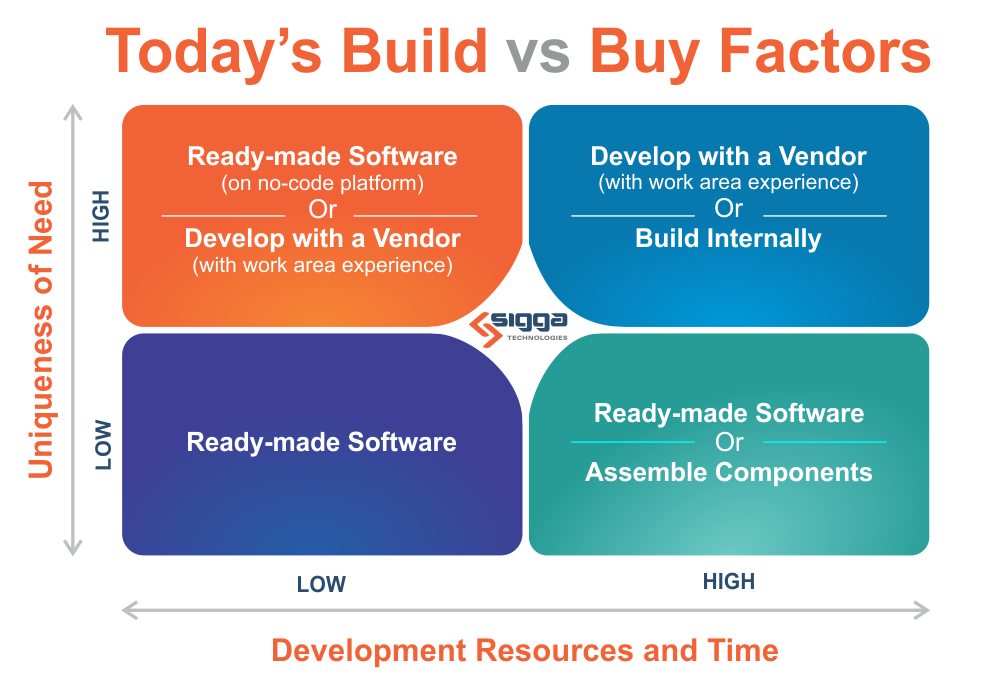
Additional Considerations Today
“The average company has 254 SaaS applications but, on average, only 45% of a company’s SaaS apps are being used on a regular basis. Moreover, 56% of all these apps are shadow IT, or owned and managed outside of IT. And the crazy part is to think that goes on top of all the software packages and systems of records they already have to run the core of their business.”
The State of SaaS Sprawl in 2021
It is unsustainable to continue to have “SaaS Sprawl” in today’s world. For decision-making and efficiency, it is critical that applications are in active use and are well integrated with legacy and core systems, like SAP. Low-code development platforms whether standalone or within an application need to include the APIs and capabilities to be easily integrated into core systems.
The Best of Both Approaches for EAM Applications
Here at Sigga, we have fully embraced the need for applications to be flexible to be modified at any time. Our ready-made, mobile EAM software comes on a fully featured no-code platform. This robust, native mobile application is a result of continued development across 15 years of deployments with 70,000 users.
We are specialized in maintenance mobile apps and software for SAP EAM. As such, we have the only no-code platform with over 200 pre-built SAP PM services. This means, you can completely avoid the costs and delays of development with SAP integration specialists. In addition, our SAP integration technology is specially designed to deliver high performance with a high volume of data and mobile users.
We are an SAP-certified global software company with 20 years of experience in helping large global companies optimize SAP with our innovative solutions and attentive support. We invest hundreds of thousands of hours annually in research & development to ensure the highest quality user experiences, ease of implementation, and security of our EAM software. As a result, some of the world’s largest companies across over 14 industries trust Sigga to improve the efficiency of their SAP-based operations.
See how Sigga EAM Empower can deliver on your digital transformation goals in operations.